Regenerative Action
In the cell tissues of mature joint chondrocytes separated from the cartilage, Jointsol® existence produced an increase of the collagen biosynthesis and proteoglycans as regards chondrocytes which have been exclusively treated with collagen hydrolysate (Graphic 3).
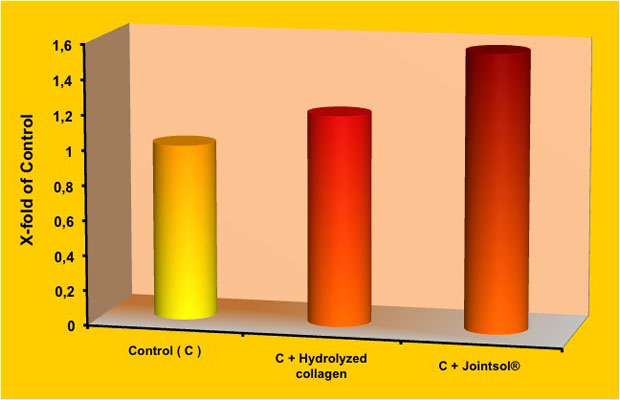
Graphic 3. Stimulation of collagen and proteoglycans production after 3 days from the chondrocytes incubation (control) with 0.5 mg/ml of collagen hydrolysate (control+collagen) or with Jointsol® (control + Jointsol®).
Considering the value 1 as reference in the control cells (without treatment), the collagen hydrolysate increased 1.2 times the production of collagen, meanwhile when the chondrocytes increased with Jointsol®, the collagen production multiplied 1.6 times, that is, Jointsol® existence produced an increase of 30% more in the collagen accumulation inside the extracellular matrix than the one produced only through the stimulation with collagen hydrolysate.
The stimulation in proteoglycans biosynthesis followed a similar procedure where Jointsol® remarkably increased the existence of these substances in the extracellular matrix compared to what has was done by the collagen hydrolysate.
The stimulating effect of matrix’s macromolecules has been confirmed through the evaluation of RNA expression (Graphic 4). The RNA expression of Type II collagen and therefore the synthesis of this protein, has been more evident in the incubated chondrocytes in Jointsol® than the ones treated with collagen hydrolysate only.
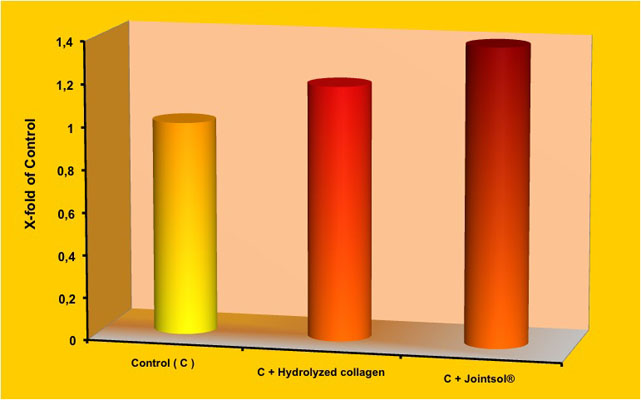
Graphic 4. Stimulation of RNA production of Type II collagen after 3 days of chondrocytes incubation (control) with 0.5 mg/ml of collagen hydrolysate (control+collagen) or with Jointsol® (control + Jointsol®).
Graphic 2. Inhibitory action of several Jointsol® concentrations on the production of metalloproteinases (MMP1 y MMP3) and interleukin 8 (IL-8)
Continue

